The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, holds an important place in history as one of the longest-lasting and most influential empires. From its rise to power to its eventual decline, the Ottoman Empire left an indelible mark on the world stage. In this article, we will explore the rise and fall of the Ottoman Empire, its cultural and technological developments, its impact on the Middle East and Europe, and its legacy.
Rise and Fall: From a Turkish Tribe to a Vast Empire
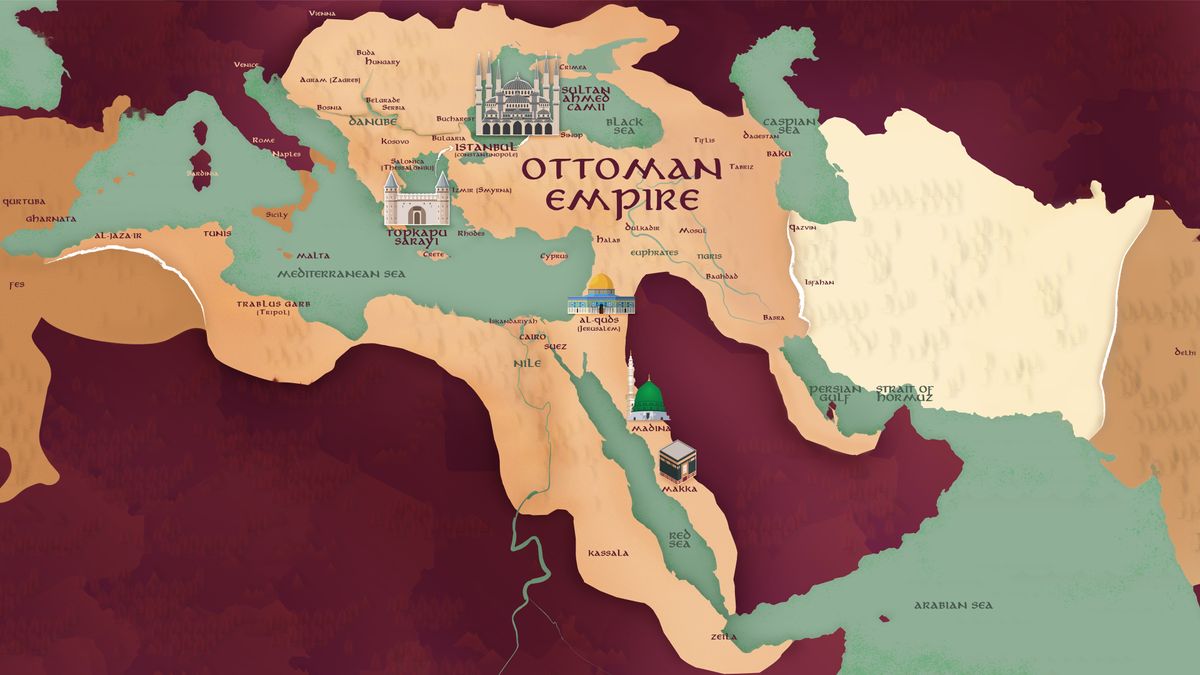
The Ottoman Empire’s story began with the rise of the Turkish tribes in Anatolia. Led by charismatic leaders like Osman Gazi, the Ottomans gradually expanded their influence, conquering neighboring territories and establishing a powerful state. With the conquest of Constantinople by Mehmed the Conqueror in 1453, the Ottomans reached the pinnacle of their power, establishing Istanbul as their capital and solidifying their rule over vast territories.
Istanbul: The Glorious Capital and Cultural Center
At the heart of the Ottoman Empire stood Istanbul, formerly known as Constantinople. This magnificent city served as the Empire’s political, economic, and cultural center. It showcased the Empire’s grandeur through architectural wonders like the Hagia Sophia, the Topkapi Palace, and the Blue Mosque. Istanbul was a city of power and a melting pot of diverse cultures, blending influences from Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
Cultural and Technological Advancements
The Ottoman Empire was a force in politics and military might and a hub of cultural and technological development. The Empire fostered a vibrant cultural scene with advancements in literature, music, art, and architecture. The Ottoman architecture, characterized by its grand mosques, elaborate palaces, and distinctive domes, remains an enduring symbol of the Empire’s artistic achievements.
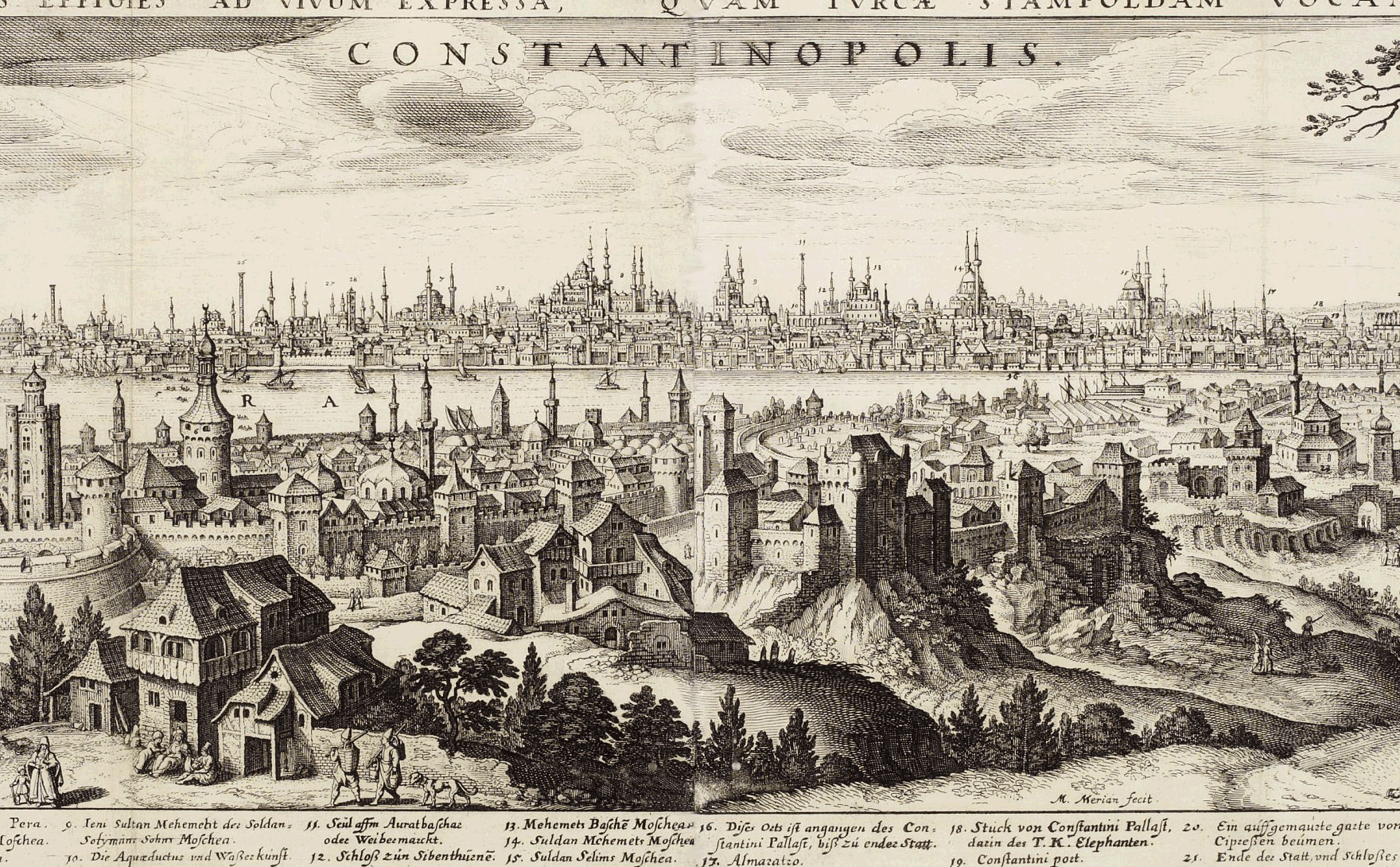

The Ottoman Empire’s Influence on the Middle East and Europe
The Ottoman Empire’s influence extended far beyond its borders, shaping the Middle East and Europe’s political, social, and cultural landscapes. The Empire’s vast territories spanned three continents, encompassing diverse ethnic and religious groups. The Ottomans introduced a system of governance that allowed for religious and cultural diversity, providing relative stability and fostering a sense of identity among the different communities.

Conclusion
The Ottoman Empire is a testament to a dynasty’s power, endurance, and cultural richness that shaped history for over six centuries. From its humble beginnings as a Turkish tribe to its vast territorial conquests, the Empire left an indelible mark on the Middle East and Europe. Istanbul, the Empire’s glorious capital, is a tangible reminder of its grandeur and cultural legacy. The Ottoman Empire’s rise and fall, its cultural and technological advancements, and its influence on the world make it a captivating subject for exploration and study.

Ottoman Empire:
What were the main achievements of the Ottoman Empire?
The Ottoman Empire's main achievements include its vast territorial expansion, architectural wonders like the Hagia Sophia, cultural advancements in literature and art, and technological developments in military warfare.
How long did the Ottoman Empire last?
The Ottoman Empire lasted over six centuries, from the late 13th century to the early 20th century.
What was the significance of Istanbul in the Ottoman Empire?
Istanbul served as the capital and cultural center of the Ottoman Empire. It showcased the empire's grandeur through magnificent structures and was a melting pot of diverse cultures.
How did the Ottoman Empire impact Europe?
The Ottoman Empire's interactions with European states had a profound impact, triggering cultural exchanges, trade relationships, and military conflicts that shaped European history.
What led to the decline of the Ottoman Empire?
The decline of the Ottoman Empire can be attributed to a combination of factors, including internal conflicts, external threats, geopolitical changes, and the rise of nationalist movements within its territories.


0 Comment